Due to issues regarding natural resources and environments as well as increasing demand for reducing CO2 emissions, a comprehensive energy modeling tool that is capable to analyze not only the performance of building envelope and HVAC system, but also lighting, water use and additional equipment loads such as elevators, has become more necessary.
The Japanese Government aims to reduce the annual CO2 emission 15% by 2020; 80% by 2050. In order to meet the large reduction in CO2 emission, an effective design tool for calculating CO2 emissions by building and for analyzing overall building energy consumption, especially for commercial buildings that emit one-third of total CO2 emission, is required. BEST (Building Energy Simulation Tool) is an effective computer simulation program for building energy research and evaluation.
BEST's Features and Effective Uses
BEST is a simulation tool that calculates and visualizes annual energy consumption of a building. The simulation includes HVAC and plumbing equipments, telecommunications and all other building loads.
It generates overall building energy consumption (annual CO2 emission) at every phase (design, construction, operation and retrofitting phase), and identifies the optimal solution (minimum) for the integrated building envelope and HVAC system.
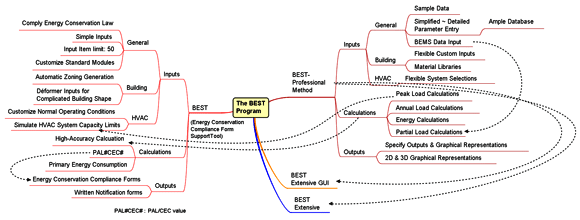
BEST consists of three methods; Simplified, Basic and Professional method. The choice of method is determined by the modeling purpose at each phase such as design (schematic, detailed, construction), operation or retrofitting phase. The numbers of accessible and changeable parameters in each method are varied. Simplified method has the least parameters while Professional method has the most.
Simplified Method: The cooling and heating peak loads and annual building energy consumption are generated by simply providing building size, type and major HVAC system types. Since the majority options are defaulted or determined by the minimum energy codes, the input parameters are minimized. Consequently, the modeling result indicates a base-case model for proposed design comparisons.
Basic Method: In addition to the information provided in Simplified Method, the more detailed inputs are possible. This method is suitable to study and to optimize the building envelope (including openings and insulations) and HVAC system.
Since April 2010, Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transportation (MLIT), Housing Bureau has been requited to submit building energy conservation measures of all newly constructing buildings with the total building area of 300 m2 or more during the construction. With supports from Housing Bureau, both Simplified and Basic methods have been developed to generate the compliance form for the building energy conservation measures. This not only reduces time and efforts on creating the compliance form, but also minimizes administrative efforts by the Bureau.
Professional Method: This method allows accessing to change all available parameters. It is capable of evaluating overall building energy use and identifying the fairly detailed optimal design solutions which include the detailed envelope selections (dimensions and constructions of glazing; singe and double glass, dimensions of Mullion eaves, insulation thickness, etc.) and the building system optimizations (HVAC system and the control, zoning, air flow, daylighting system and the lighting control, etc.)
For operational and retrofitting phases, BEST identifies the most appropriate solution to improve building performance based on detailed HVAC system data, actual building operational schedule and measured energy consumptions. The optimal solution is selected amongst various energy conservation possibilities by evaluating performances that can be seen in hard and soft.
Figure -1: Summary of BEST Program